Guide to Trading Crude Oil: Strategies, Factors, and Market Dynamics
Crude oil is one of the most actively traded commodities in the world, offering significant opportunities for traders. Its importance in various industries, geopolitical factors, and global demand make it a highly volatile and lucrative market. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of trading crude oil, exploring strategies, key factors influencing prices, and market dynamics.
I. Understanding Crude Oil
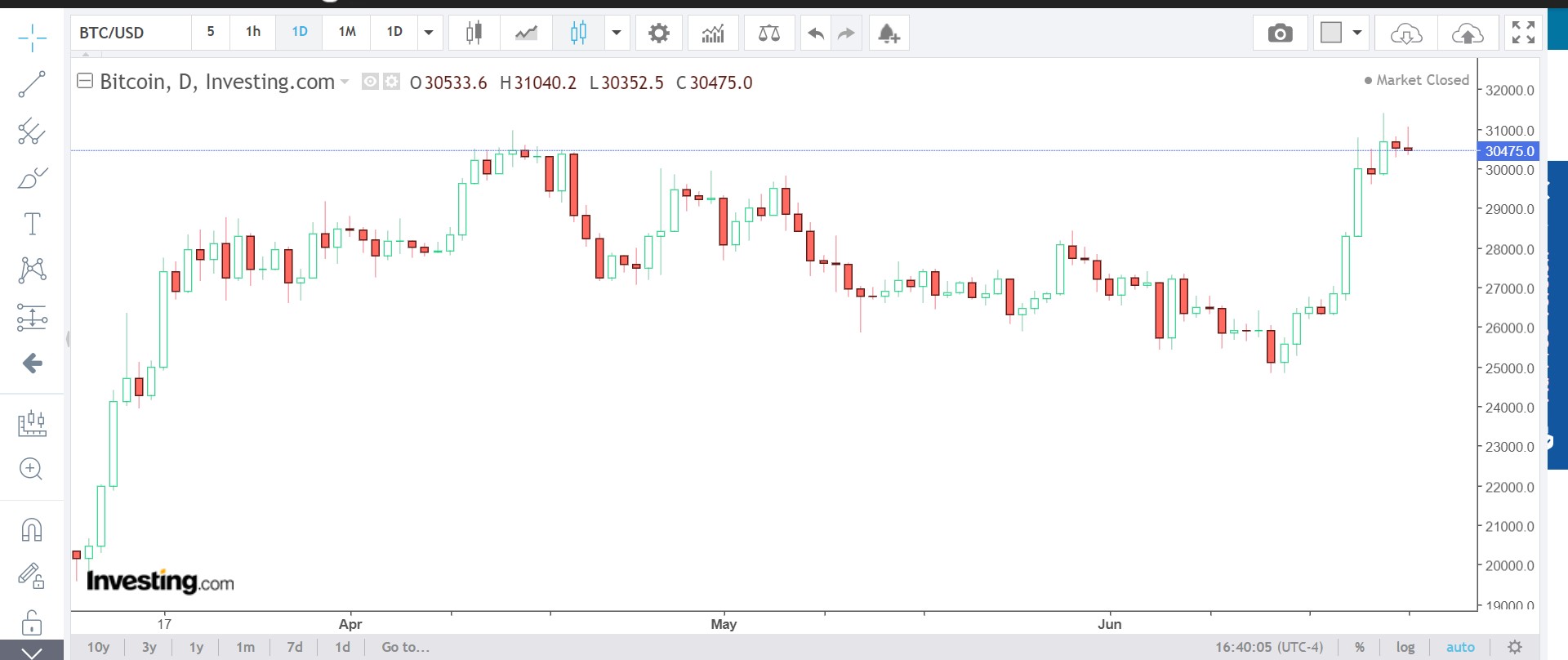
Crude oil is a naturally occurring fossil fuel composed of hydrocarbon deposits found beneath the Earth’s surface. It is extracted through drilling and serves as a vital source of energy for transportation, manufacturing, and other sectors. The two primary benchmarks for crude oil trading are Brent Crude and West Texas Intermediate (WTI).
II. Factors Influencing Crude Oil Prices
1. Supply and Demand Dynamics: The balance between global supply and demand plays a crucial role in determining crude oil prices. Factors such as OPEC production decisions, geopolitical tensions, economic growth rates, and weather conditions can impact supply levels.
2. OPEC Actions: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) consists of major oil-producing nations that collectively influence global oil prices through production quotas. OPEC’s decisions on output levels can significantly impact crude oil prices.
3. Geopolitical Events: Political instability, conflicts, sanctions, and trade disputes among major oil-producing nations can disrupt supply chains and affect crude oil prices.
4. Economic Indicators: Macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth rates, inflation levels, interest rates, and currency exchange rates can influence crude oil prices. Strong economic growth often leads to increased demand for oil.
5. Inventories and Storage Levels: Crude oil inventories serve as an important indicator of supply-demand imbalances. High inventory levels can exert downward pressure on prices, while low inventories can lead to price spikes.
III. Trading Strategies for Crude Oil
1. Technical Analysis: Traders often use technical indicators, charts, and patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Moving averages, trend lines, and oscillators are commonly employed tools in analyzing crude oil price movements.
2. Fundamental Analysis: This approach involves analyzing supply-demand fundamentals, geopolitical events, economic data, and other factors to predict future price movements. Understanding the impact of OPEC decisions, inventory reports, and economic indicators is crucial for fundamental analysis.
3. Spread Trading: Spread trading involves taking positions in two different but related crude oil contracts to profit from price differentials between them. For example, traders may go long on Brent Crude and short on WTI if they anticipate a widening spread between the two benchmarks.
4. News Trading: Rapidly reacting to news events that impact crude oil prices can be a profitable strategy. Traders closely monitor news releases related to OPEC decisions, geopolitical tensions, economic data, and weather forecasts to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations.
IV. Risks and Risk Management
Trading crude oil involves inherent risks that traders must manage effectively. Price volatility, geopolitical uncertainties, unexpected supply disruptions, and market manipulation are some of the risks associated with this market. Implementing risk management strategies such as setting stop-loss orders, diversifying portfolios, and staying updated with market news can help mitigate these risks.
Crude oil is highly volatile and makes great opportunities but also dangerous to trade if not clear with risk management plan.
Simon Frandsen / Pyjamastraders